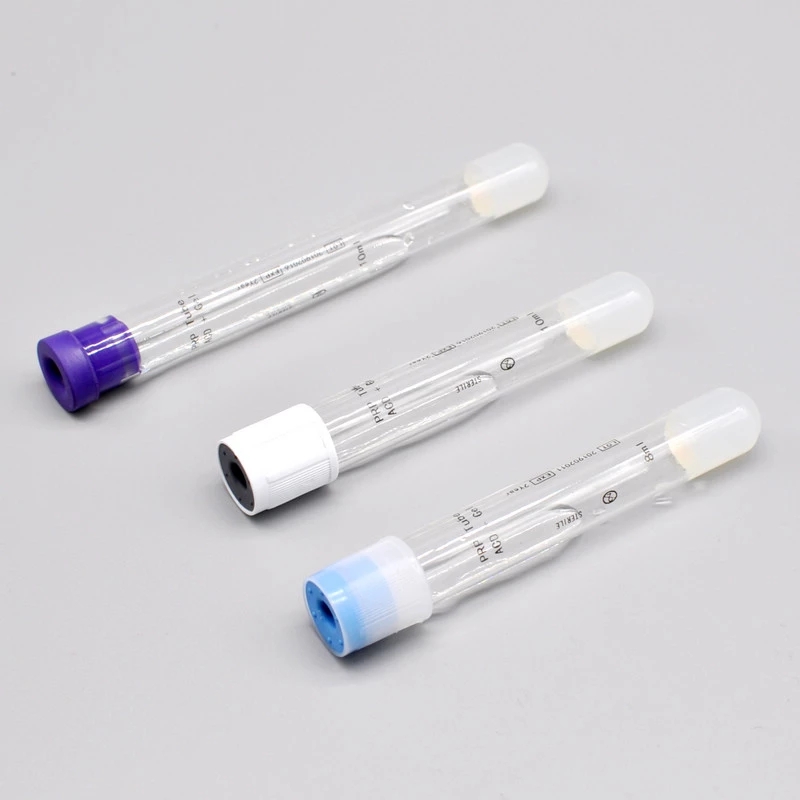
PRP Tube with Gel
Short Description:
Abstract.Autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP) gel is increasingly used in the treatment of a variety of soft and bony tissue defects, such as accelerating bone formation and in the management of chronic non-healing wounds.
All blood cells derive from a common pluripotent stem cell, which differentiates into different cell lines. Each of these cell series contains precursors that can divide and mature.
Platelets, also called thrombocytes, develop from the bone marrow. Platelets are nucleated, discoid cellular elements with different sizes and a density of approximately 2 μm in diameter, the smallest density of all blood cells. The physiological count of platelets circulating in the blood stream ranges from 150,000 to 400,000 platelets per μL.
Platelets contain several secretory granules that are crucial to platelet function. There are 3 types of granules: dense granules, o-granules, and lysosomes. In each platelet there are approximately 50-80 granules, the most abundant of the 3 types of granules.
Platelets are primarily responsible for the aggregation process. The main function is to contribute to homeostasis trough 3 processes: adhesion, activation, and aggregation. During a vascular lesion, platelets are activated, and their granules release factors that promote coagulation.
Platelets were thought to have only hemostatic activity, although in recent years, scientific research and technology has provided a new perspective on platelets and their functions. Studies suggest that platelets contain an abundance of GFs and cytokines that can affect inflammation, angiogenesis, stem cell migration, and cell proliferation.
PRP is a natural source of signaling molecules, and upon activation of platelets in PRP, the P-granules are granulated and release the GFs and cytokines that will modify the per cellular microenvironment. Some of the most important GFs released by platelets in PRP include vascular endothelial GF, fibroblast GF (FGF), platelet-derived GF, epidermal GF, hepatocyte GF, insulin-like GF 1, 2 (IGF-1, IGF-2), matrix metalloproteinase 2, 9, and interleukin 8.