-

Blood Collection Tube–Black Tube–ESR Test
ESR tubes are mainly used for blood sample collection and anticoagulation during erythrocyte sedimentation rate test.It contains 3.8% (0.129mol/L) sodium citrate buffer which mixed with blood in a ratio of 4:1.
-
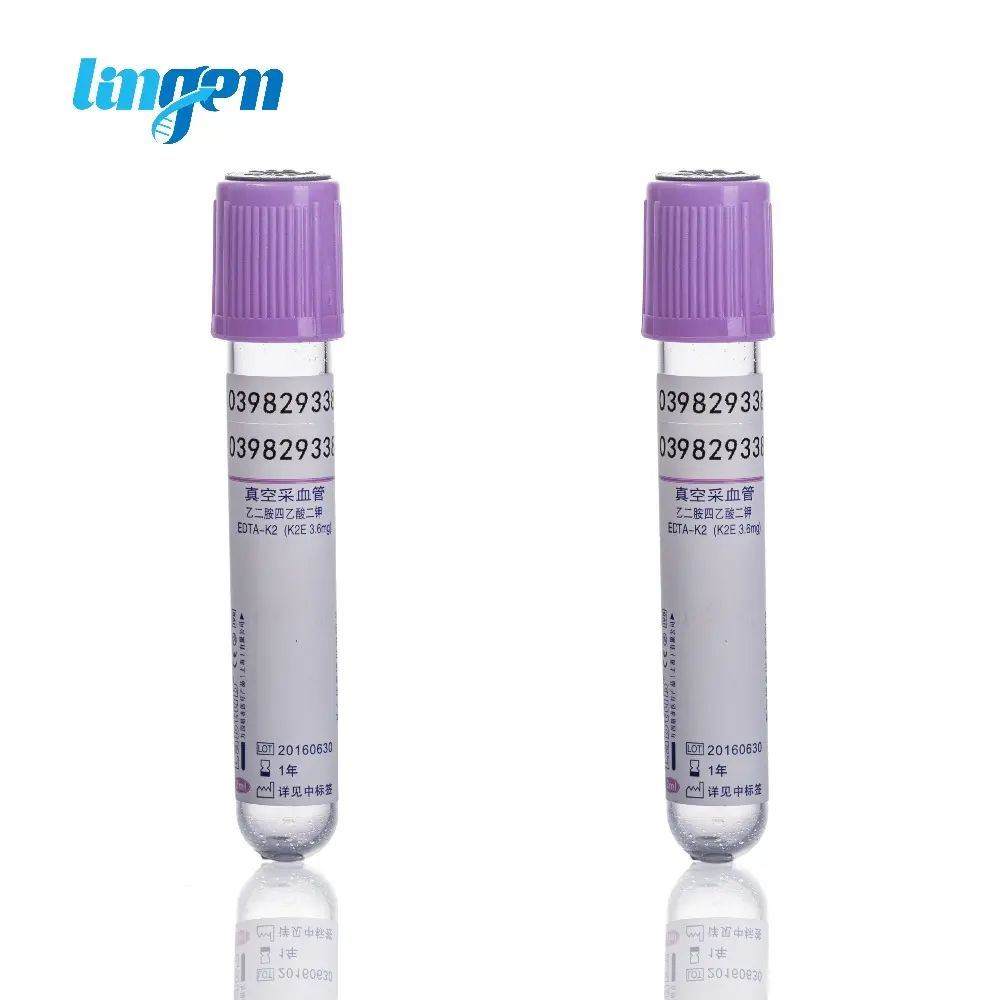

Blood Collection Tube–EDTA Tube– edta 2k/3k
The blood routine tube is widely used in clinical Hematology examination and is suitable for various blood cell analyzers. It provides a comprehensive and detailed protection plan for blood cells, especially with the use of inner wall biomimetic membrane treatment technology, effectively preventing platelet aggregation and activation, preventing coagulation, and protecting the shape and volume of blood cells from being affected for a long time.
-
Blood Collection Tube–1:9 Blue Tube–Coagulation Test
Coagulation tube, is used to obtain plasma samples for the coagulation test. It contains 3.2% (0.109 mol/L) buffered sodium citrate solution. Blood and sodium citrate are mixed in a ratio of 9:1,ensure the validity of the test results. Due to the low toxicity of sodium citrate, it is also used for blood preservation.
-
Blood Collection Tube–Clot Activator–Rapid Serum Test
Clot Activator tube, is used to collect serum samples for biochemical and immunological testing, and can be used for rapid outpatient, emergency serum biochemical tests. The time to complete clot shrinkage is around 20 minutes, the centrifugation speed is 3500-4000 rpm, the centrifugation time is 5 minutes, and the recommended storage temperature is 4°C-25°C.After blood collection, immediately invert and mix 8 times, let stand for 20 minutes,then finally centrifuge.
-
Blood Collection Tube–Grey Cap–Glucose Tube
The combination of sodium fluoride and anticoagulant tubes are used to obtain highly stable plasma for blood glucose testing. Sodium fluoride is a glucose degradation inhibitor, which has the effect of inhibiting glucose metabolism and degradation. The optional anticoagulants are potassium oxalate, EDTA and heparin sodium, which can prevent blood clotting and avoid hemolysis.Used for blood glucose test.
-
Blood Collection Tube–Separation Gel–Rapid Serum Test
Gel&Clot Activator tube is used for serum biochemistry, drug detection and immunology, etc. Coagulant is finely coated on the inner wall of which can shorten the blood coagulation time.The biochemical properties and chemical composition of the serum do not change significantly within 48 hours.Centrifuge after 20 minutes of rest, the recommended storage temperature is 4°C-25°C.
-
Blood Collection Tube–Sodium Heparin–Rapid Plasma Test
Heparin tube is used for the collection of blood samples for clinical plasma biochemical and blood rheology determination, without affecting the volume of red blood cells and causing hemolysis. The operating temperature range is wide, the plasma separation speed is fast, and the compatibility with serum specimen indicators is strong. In addition to the characteristics of heparin sodium, lithium heparin can also be used for the detection of trace elements.
-
Blood Collection Tube–Lithium Heparin–Rapid Plasma Test
Gel and Heparin tubes are anticoagulant tubes used to obtain high quality plasma samples for rapid emergency biochemical testing. There are some gels at the bottom of the test tube, which are used to separate plasma and blood cells. The exchange of substances can be prevented, so that the obtained plasma is free from blood cell contamination, making the results accurate.
-

Blood Collection Tube–Plain Tube–No Additive Tube
The red cap is called ordinary serum tube, and the blood collection vessel does not contain any additives. It is used for routine serum biochemistry, blood bank and serological related tests.
